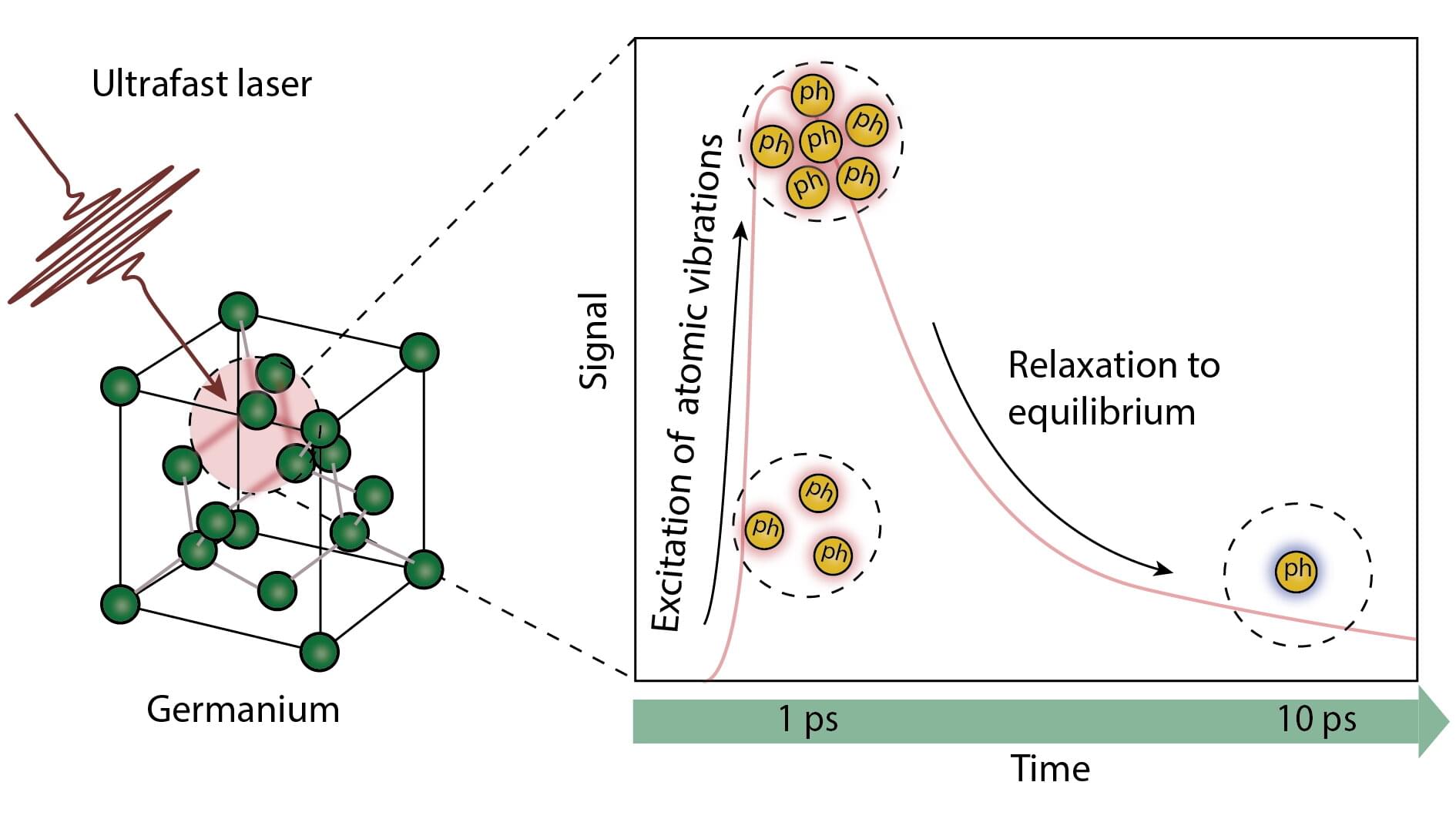
Whether in a smartphone or laptop, semiconductors form the basis of modern electronics and accompany us constantly in everyday life. The processes taking place inside these materials are the subject of ongoing research. When the electrons in a semiconductor material are activated using light or an electrical voltage, the excited electrons also set the atomic lattice in motion. This results in collective vibrations of the atoms, known as phonons or lattice vibrations, which interact with each other and with the electrons themselves.
These tiny lattice vibrations play a vital role in how energy flows and dissipates through the material—in other words, in how efficiently the energy is redistributed and how strongly the material heats up. Different approaches can be used to control and monitor the propagation of lattice vibrations—and therefore to make the semiconductor more effective and more efficient.
Detailed knowledge of the mechanisms of energy loss and potential overheating is essential in order to design new materials and devices that heat up less, recover faster or respond to external excitation more precisely. A team led by Professor Ilaria Zardo from the University of Basel reports on the unprecedented accuracy they achieved in measurements of energy flow processes within the semiconductor germanium, which is frequently used in computer technology. Their paper is published in Advanced Science.