This will create new types of jobs especially in software industries.
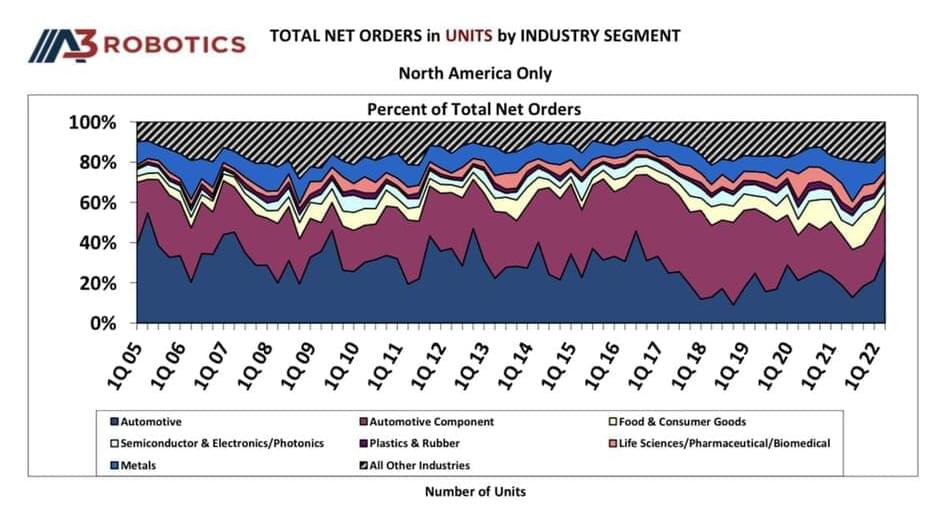
ANN ARBOR, Mich.—(BUSINESS WIRE)—For the third-straight quarter, robot sales in North America hit a record high, driven by a resurgence in sales to automotive companies and an ongoing need to manage increasing demand to automate logistics for e-commerce. According to the Association for Advancing Automation, of the 12,305 robots sold in Q2 2022, 59% of the orders came from the automotive industry with the remaining orders from non-automotive companies largely in the food & consumer goods industry, which saw a 13% increase in unit orders over the same period, April through June, in 2021.
Robot sales hit new record in North America for 3rd straight quarter: Includes renewed surge in #automotive and continued uptake of #robotics and #automation in food and consumer goods industries driven by #ecommerce, industry group @a3automate reports.
“While automotive entities have long been the frontrunner in deploying robotics and automation, the last few years have seen food & consumer goods, life sciences and other industries grow at even higher rates,” said A3 President Jeff Burnstein. “While this quarter shows a marked shift back to historic norms with more robots going to automotive than to any other industry, the continued growth of robotics in food & consumer goods companies especially demonstrates the ongoing need to automate warehouse logistics for handling the exploding growth of e-commerce. We’re excited to share the latest on robots in the logistics space at our upcoming Autonomous Mobile Robots & Logistics Week in Boston in October.”