“I am committed to the notion that the past predicts the present,” Larsen tells Inverse, “and we need to understand that past to understand the world we live in now.”
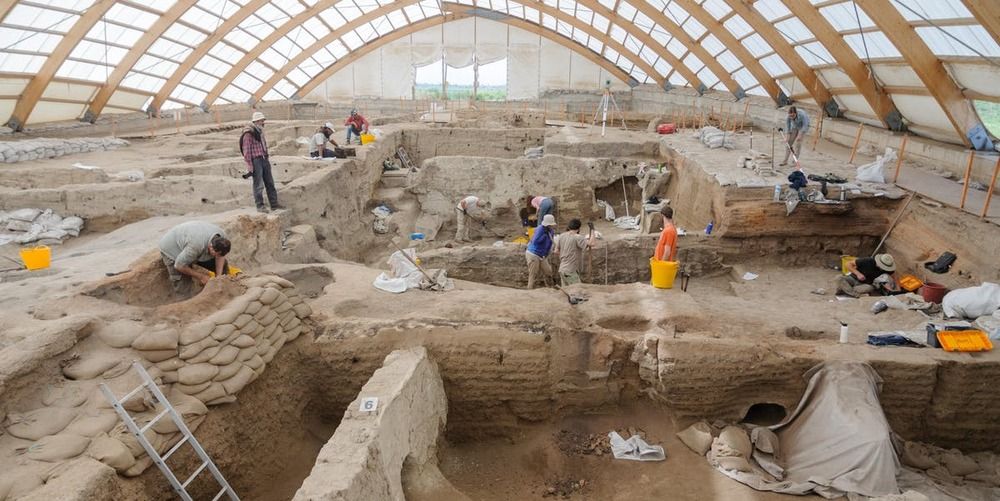
Larsen has had a longstanding interest in the health and lifestyle of early farmers — those who were working around the Neolithic transition from hunting and gathering to farming. So when Ian Hodder, Ph.D., an archeologist who leads the Çatalhöyük Research Project, invited him to join the project in 2004, he quickly accepted the opportunity.
This new study is based on 25 years of findings linked to the human remains found in Çatalhöyük. Dating of remains shows that the population there grew to its peak in the period from 6,700 to 6,500 B.C. and then declined rapidly. That decline is likely linked to the evidence of disease and malnutrition Larsen and colleagues found in the remains.