Interesting research paper on a new nanobot technology. I’m watching for ways in which suitable substrates for mind uploading can be constructed, and DNA self-guided assembly has potential.
Here are some excerpts and a weblink to the paper:
“…Chemical approaches have opened synthetic routes to build dynamic materials from scratch using chemical reactions, ultimately allowing flexibility in design…”
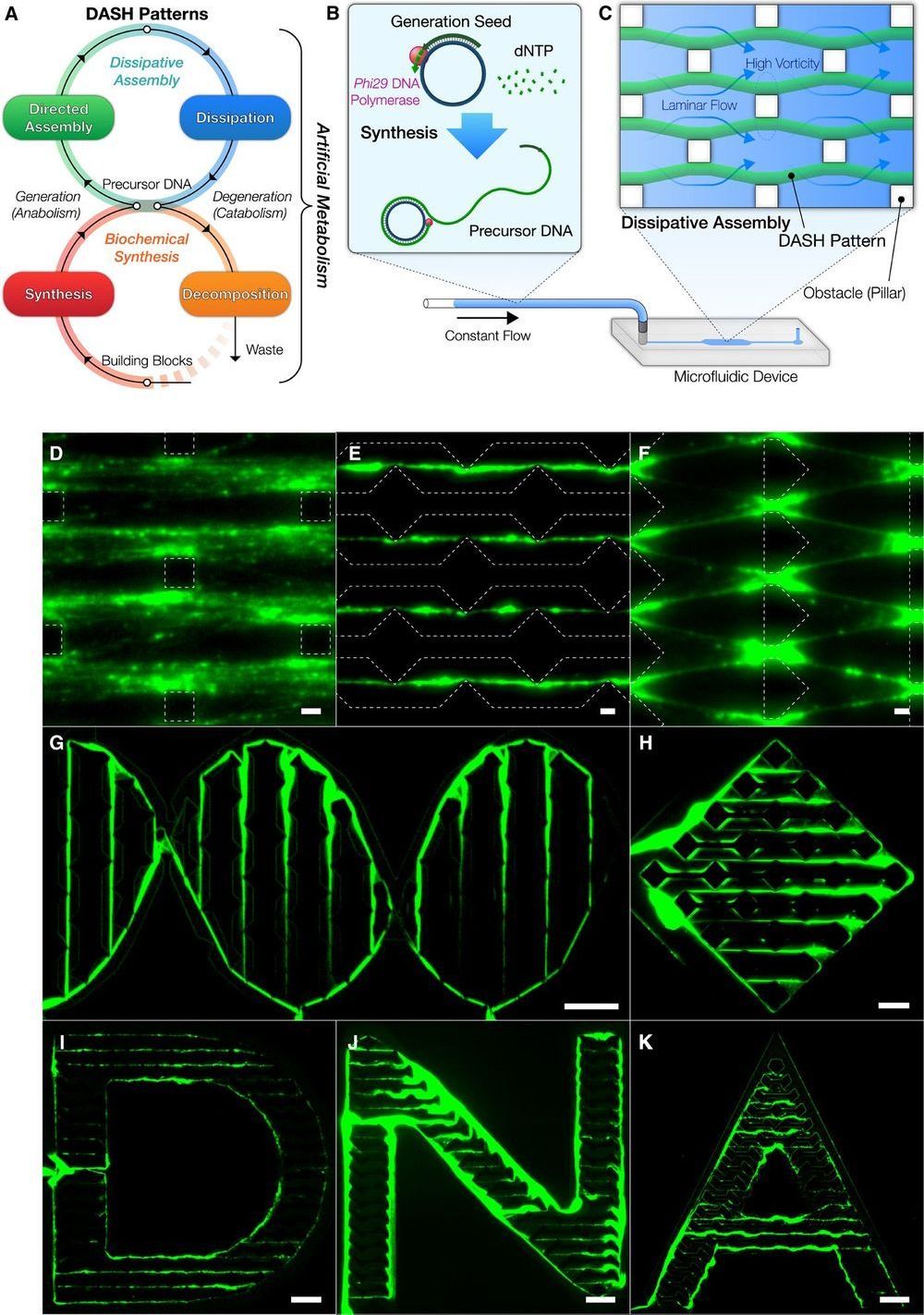
… As a realization of this concept, we engineered a mechanism termed DASH—DNA-based Assembly and Synthesis of Hierarchical materials—providing a mesoscale approach to create dynamic materials from biomolecular building blocks using artificial metabolism. DASH was developed on the basis of nanotechnology that uses DNA as a generic material ranging from nanostructures to hydrogels, for enzymatic substrates, and as linkers between nanoparticles…”
“…Next, to illustrate the potential uses of self-generated materials, we created various hybrid functional materials from the DASH patterns. The DASH patterns served as a versatile mesoscale scaffold for a diverse range of functional nanomaterials beyond DNA, ranging from proteins to inorganic nanoparticles, such as avidin, quantum dots, and DNA-conjugated gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) (Fig. 4D, figs. S37 and S38, and Supplementary Text). The generated patterns were also rendered functional with catalytic activity when conjugated with enzymes (figs. S39 and S40 and Supplementary Text). We also showed that the DNA molecules within the DASH patterns retained the DNA’s genetic properties and that, in a cell-free fashion, the materials themselves successfully produced green fluorescent proteins (GFPs) by incorporating a reporter gene for sfGFP (Fig. 4E and figs. S9 and S41) (40). The protein production capability of the materials established the foundation for future cell-free production of proteins, including enzymes, in a spatiotemporally controlled manner.
…” Our implementation of the concept, DASH, successfully demonstrated various applications of the material. We succeeded in constructing machines from this novel dynamic biomaterial with emergent regeneration, locomotion, and racing behaviors by programming them as a series of FSAs. Bottom-up design based on bioengineering foundations without restrictions of life fundamentally allowed these active and programmable behaviors. It is not difficult to envision that the material could be integrated as a locomotive ele-ment in biomolecular machines and robots. The DASH patterns could be easily recognized by naked eyes or smartphones, which may lead to better detection technologies that are more feasible in point-of-care settings. DASH may also be used as a template for other materials, for example, to create dynamic waves of protein expression or nanoparticle assemblies. In addition, we envision that further expansion of artificial metabolism may be used for self-sustaining structural components and self-adapting substrates for chemical production pathways. Ultimately, our material may allow the construction of self-reproducing machines through the production of enzymes from generated materials that, in turn, reproduce the material. Our biomaterial powered by artificial metabolism is an important step toward the creation of “artificial” biological systems with dynamic, life-like capabilities.”…