Due to the groundbreaking work in superlongevity by Dr David Sinclair and Yuancheng Ryan Lu on the Information Theory of Aging and how epigenetic therapy can be used to reverse aging, I suddenly have a compelling interest in epigenetics. Here is a recent research article that I’d recommend on.
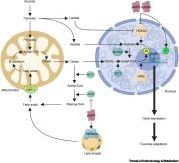
Epigenetics can be defined as ‘the structural adaptation of chromosomal regions so as to register, signal, or perpetuate altered activity states.’ Increased transcription of key regulatory, metabolic, and myogenic genes is an early response to exercise and is important in mediating subsequent adaptations in skeletal muscle. DNA hypomethylation and histone hyperacetylation are emerging as important crucial events for increased transcription. The complex interactions between multiple epigenetic modifications and their regulation by metabolic changes and signaling events during exercise, with implications for enhanced understanding of the acute and chronic adaptations to exercise, are questions for further investigation.