‘Assembly theory’ aims to explain evolution without biology. Is it a dazzling breakthrough or an attempt to answer questions nobody asked?


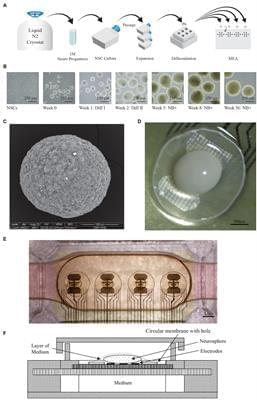
Wetware computing and organoid intelligence is an emerging research field at the intersection of electrophysiology and artificial intelligence. The core concept involves using living neurons to perform computations, similar to how Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) are used today. However, unlike ANNs, where updating digital tensors (weights) can instantly modify network responses, entirely new methods must be developed for neural networks using biological neurons. Discovering these methods is challenging and requires a system capable of conducting numerous experiments, ideally accessible to researchers worldwide. For this reason, we developed a hardware and software system that allows for electrophysiological experiments on an unmatched scale. The Neuroplatform enables researchers to run experiments on neural organoids with a lifetime of even more than 100 days. To do so, we streamlined the experimental process to quickly produce new organoids, monitor action potentials 24/7, and provide electrical stimulations. We also designed a microfluidic system that allows for fully automated medium flow and change, thus reducing the disruptions by physical interventions in the incubator and ensuring stable environmental conditions. Over the past three years, the Neuroplatform was utilized with over 1,000 brain organoids, enabling the collection of more than 18 terabytes of data. A dedicated Application Programming Interface (API) has been developed to conduct remote research directly via our Python library or using interactive compute such as Jupyter Notebooks. In addition to electrophysiological operations, our API also controls pumps, digital cameras and UV lights for molecule uncaging. This allows for the execution of complex 24/7 experiments, including closed-loop strategies and processing using the latest deep learning or reinforcement learning libraries. Furthermore, the infrastructure supports entirely remote use. Currently in 2024, the system is freely available for research purposes, and numerous research groups have begun using it for their experiments. This article outlines the system’s architecture and provides specific examples of experiments and results.
The recent rise in wetware computing and consequently, artificial biological neural networks (BNNs), comes at a time when Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) are more sophisticated than ever.
The latest generation of Large Language Models (LLMs), such as Meta’s Llama 2 or OpenAI’s GPT-4, fundamentally rely on ANNs.
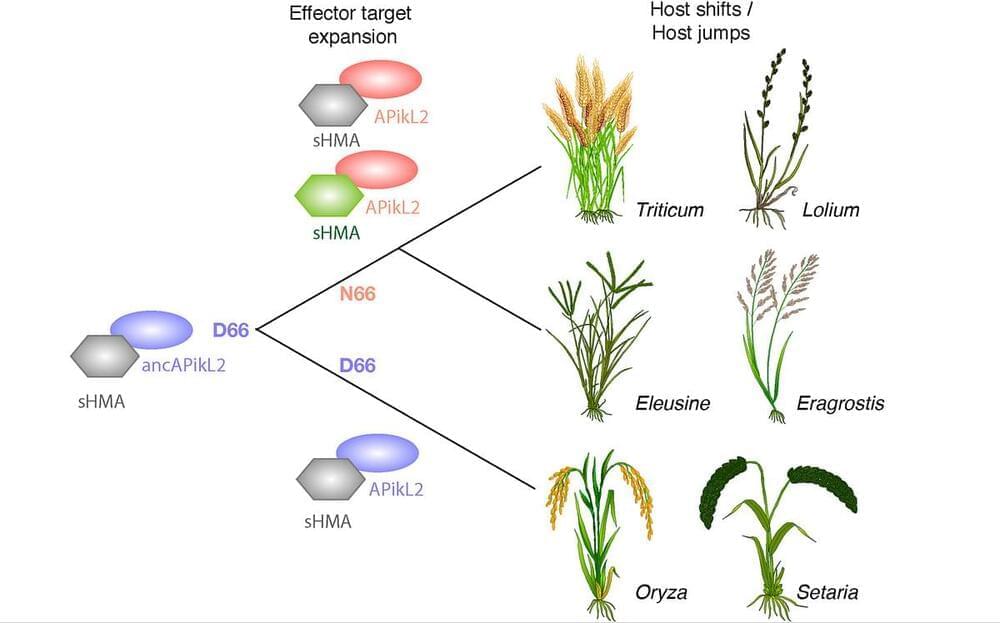
In recent years, my lab — or perhaps it’s just me — has developed an obsession with evolutionary transitions. The view that every gene originates from an ancestral state and undergoes impactful changes through its evolutionary journey, whether it’s the gain or loss of an activity or function. The challenge lies in meticulously mapping out these key evolutionary innovations that have significantly influenced function. Addressing this challenge is not merely interesting but absolutely essential in biology. Our aim as biologists transcends understanding how biological systems operate; we seek to unravel how they came to be. And the two questions are more connected than many think.
This post stems from my observation that molecular biologists sometimes appear indifferent to evolution, questioning its relevance to mechanistic research. It baffles me why the centrality of evolution in biology isn’t apparent to some. Maybe they’ve never taken a course on the subject, or perhaps they’ve never fully appreciated the profound concept that every organism and every gene is connected through an unbroken chain of descent to countless ancestors. This perspective holds profound implications for mechanistic molecular biology.
If you already appreciate the link between evolutionary biology and molecular mechanisms, you might find this post to be music to your ears. However, if you’re among those who question the value of evolutionary biology, I encourage you to stay with me; you might discover its significance in ways you hadn’t considered before.
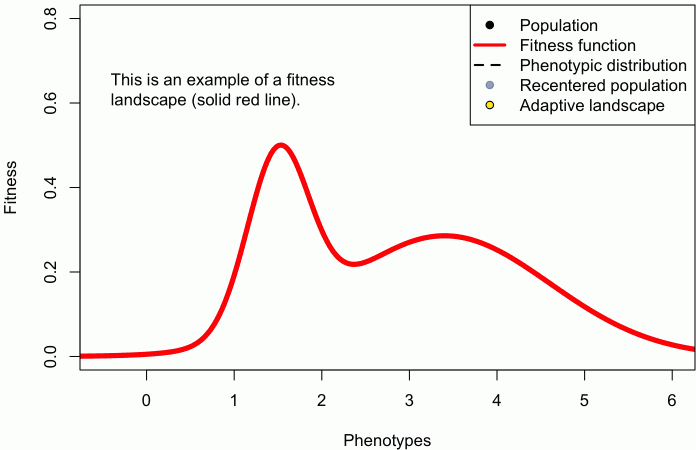
When I started my postdoc in 1998, I think it is safe to say that the Holy Grail (or maybe Rosetta Stone) for many evolutionary biologists was a concept called the Adaptive Landscape. The reason for such exalted status is that the adaptive landscape was then – and remains – the only formal quantitative way to predict and interpret an adaptive radiation of few organisms into many. I was heavily indoctrinated into this framework — as my postdoc was at UBC during precisely the time when Dolph Schluter was writing his now-classic book The Ecology of Adaptive Radiation.
Researchers have developed a new method that uses attosecond core-level spectroscopy to capture molecular dynamics in real time.
The mechanisms behind chemical reactions are complex, involving many dynamic processes that affect both the electrons and the nuclei of the involved atoms. Frequently, the strongly coupled electron and nuclear dynamics trigger radiation-less relaxation processes known as conical intersections. These dynamics underpin many significant biological and chemical functions but are notoriously difficult to detect experimentally.
The challenge in studying these dynamics stems from the difficulty of tracing the nuclear and electronic motion simultaneously. Their dynamics are intertwined and occur on ultrafast timescales, which has made capturing the molecular dynamical evolution in real time a major challenge for both physicists and chemists in recent years.



“Geometry is destiny”
How a simple cell produces remarkably complex behavior, all without a nervous system.
Combining a deep curiosity and “recreational biology,” Stanford researchers have discovered how a simple cell produces remarkably complex behavior, all without a nervous system. It’s origami, they say.

Strange underwater icicles form in the Earth’s coldest regions and freeze living organisms in place.