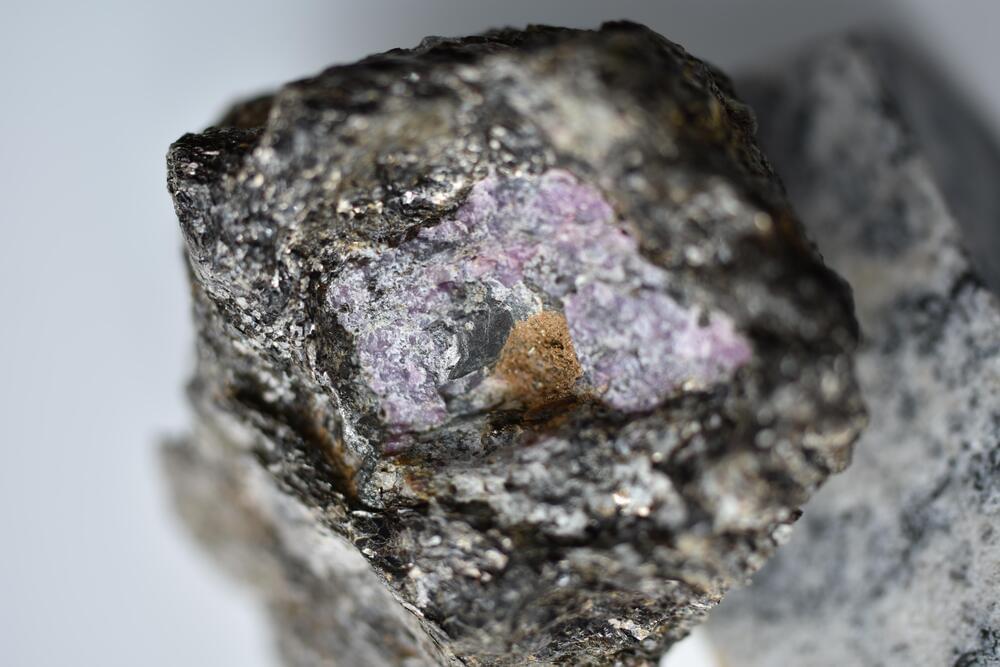
We explore Artificial Intelligence (AI) through Neuromorphic Computing with computer chips that emulate the biological neurons and synapses in the brain. Neuro-biological chip architectures enable machines to solve very different kinds of problems than traditional computers, the kinds of problems we previously thought only humans could tackle.
Our guest today is Kelsey Scharnhorst. Kelsey is an Artificial Neural Network Researcher at UCLA. Her research lab (Gimzewski Lab under James Gimzewski) is focused on creating neuromorphic computer chips and further developing their capabilities.
We’ll talk with Kelsey about how neuromorphic computing is different, how neural-biological computer architecture works, and how it will be used in the future.
Podcast version at: https://is.gd/MM_on_iTunes.
Gimzewski Lab (UCLA Neuromorphic Lab): http://gim.chem.ucla.edu.
Kelsey on LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/kelseyscharnhorst.
__________