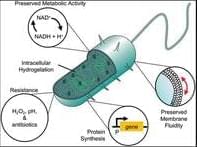
Synthetic biology has made major strides towards the holy grail of fully programmable bio-micromachines capable of sensing and responding to defined stimuli regardless of their environmental context. A common type of bio-micromachines is created by genetically modifying living cells.[ 1 ] Living cells possess the unique advantage of being highly adaptable and versatile.[ 2 ] To date, living cells have been successfully repurposed for a wide variety of applications, including living therapeutics,[ 3 ] bioremediation,[ 4 ] and drug and gene delivery.[ 5, 6 ] However, the resulting synthetic living cells are challenging to control due to their continuous adaption and evolving cellular context. Application of these autonomously replicating organisms often requires tailored biocontainment strategies,[ 7-9 ] which can raise logistical hurdles and safety concerns.
In contrast, nonliving synthetic cells, notably artificial cells,[ 10, 11 ] can be created using synthetic materials, such as polymers or phospholipids. Meticulous engineering of materials enables defined partitioning of bioactive agents, and the resulting biomimetic systems possess advantages including predictable functions, tolerance to certain environmental stressors, and ease of engineering.[ 12, 13 ] Nonliving cell-mimetic systems have been employed to deliver anticancer drugs,[ 14 ] promote antitumor immune responses,[ 15 ] communicate with other cells,[ 16, 17 ] mimic immune cells,[ 18, 19 ] and perform photosynthesis.