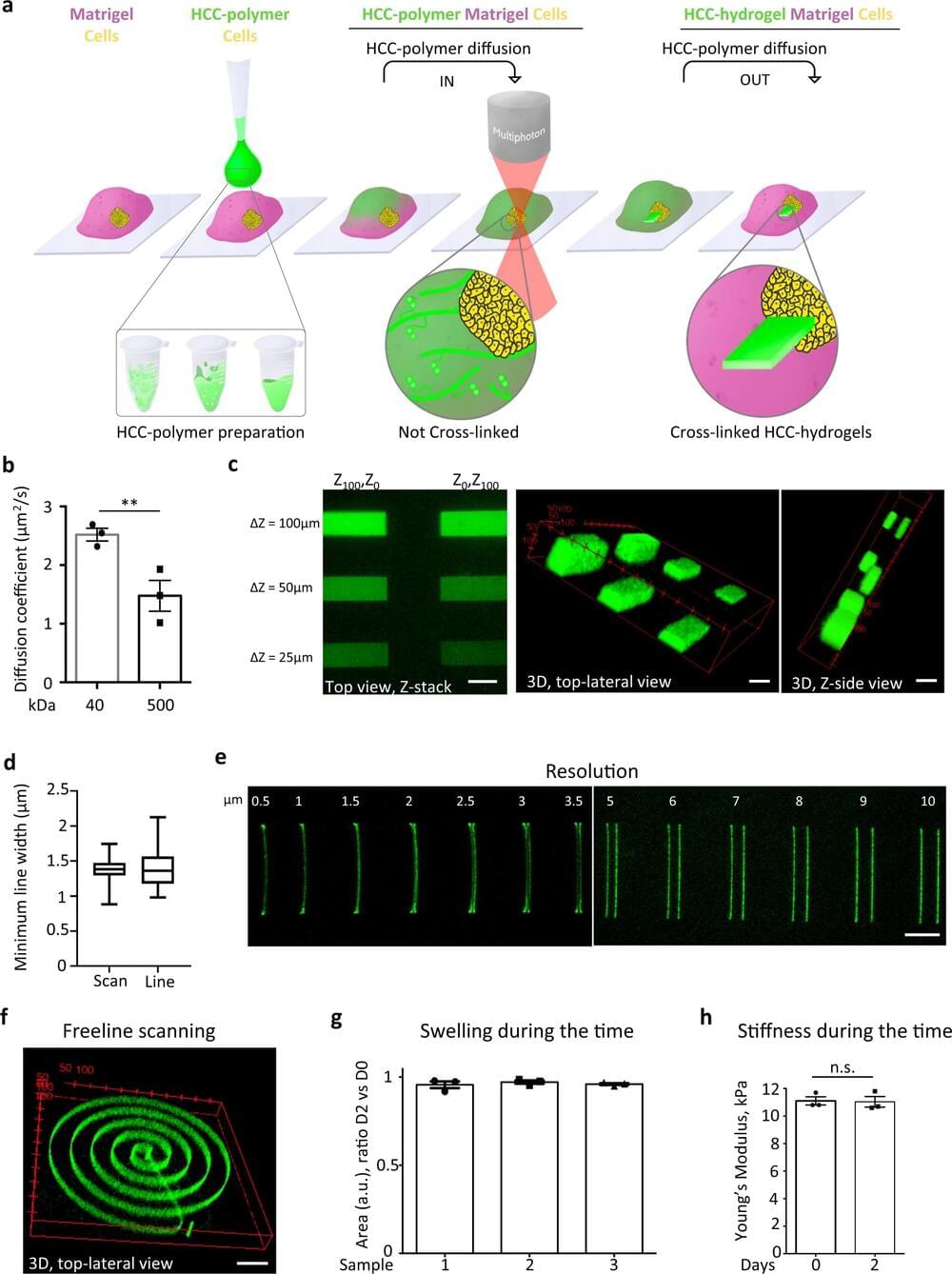
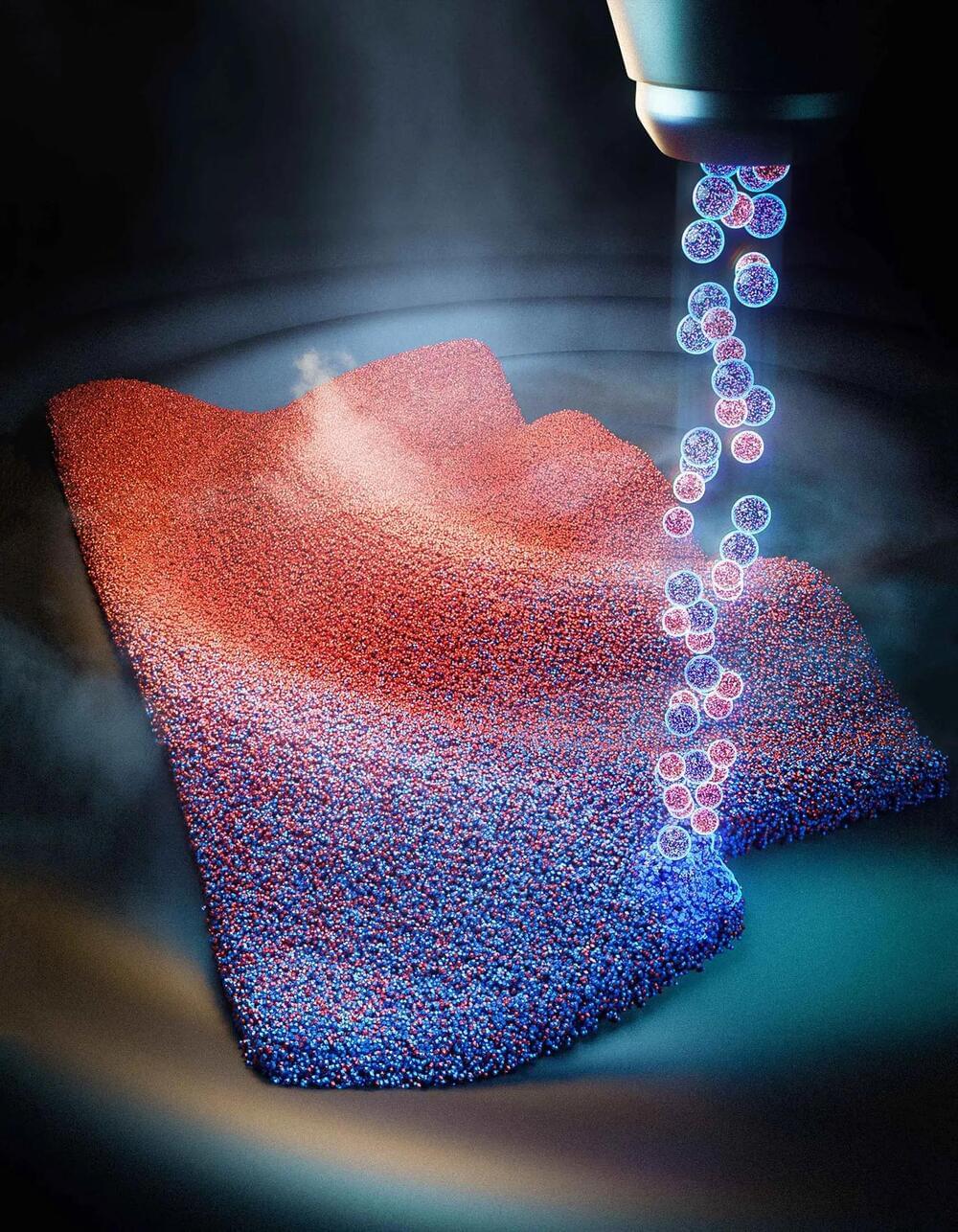
Scientists from the NIHR Great Ormond Street Hospital Biomedical Research Centre (a collaboration between GOSH and UCL), London, and University of Padova, Italy, have shown for the first time how 3D printing can be achieved inside “mini-organs” growing in hydrogels—controlling their shape, activity, and even forcing tissue to grow into “molds.”
This can help teams study cells and organs more accurately, create realistic models of organs and disease, and even better understand how cancer spreads through different tissues.
A particularly promising area of research at the Zayed Centre for Research (a partnership between Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH), GOSH Charity and University College London Great Ormond Street Institute of Child Health (UCL GOS ICH)) is organoid science—the creation of micro-versions of organs like the stomach, the intestines and the lungs.