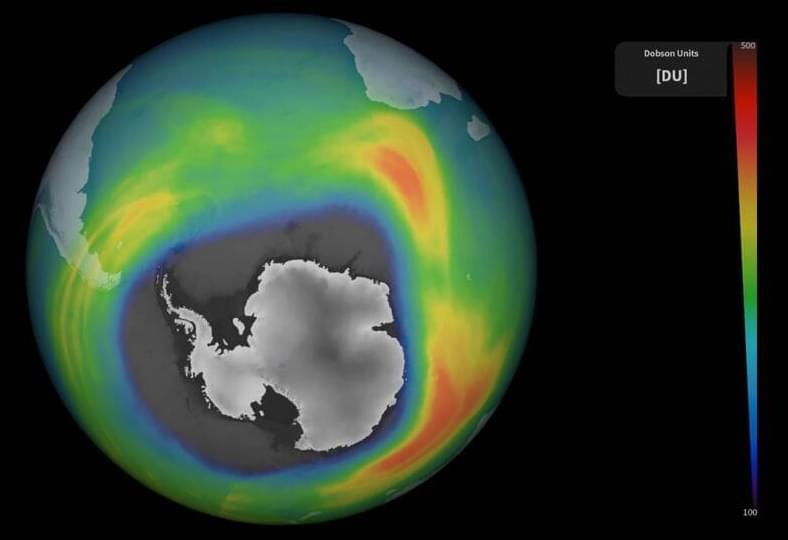
One of the largest ozone holes on record has been observed over Antarctica this year, according to measurements from the European Space Agency’s Copernicus Sentinel-5P satellite.
A lower concentration of O3 molecules
The ozone hole is a section of the stratosphere of Earth where there is a markedly lower concentration of ozone (O3) molecules. The ozone layer is severely diminishing in some parts of the stratosphere, although it is not technically a hole. By absorbing the bulk of the sun’s harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation, the ozone layer, a region of the Earth’s atmosphere with a relatively high concentration of ozone molecules, plays a crucial role in safeguarding life on the planet.