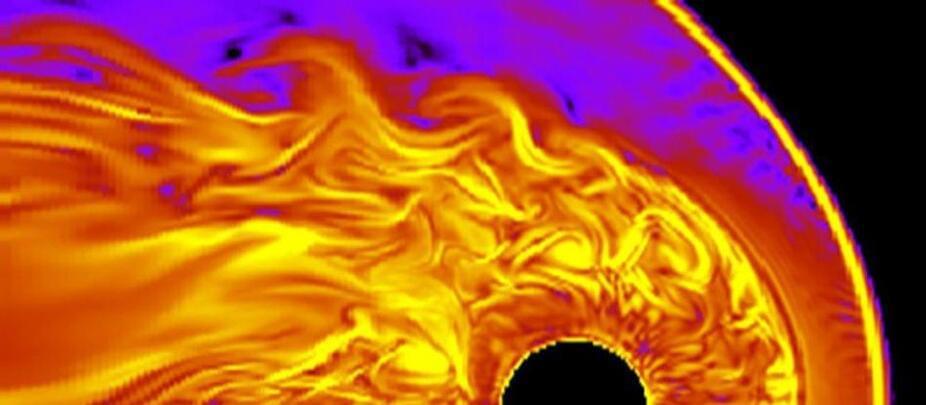
Giant waves have been found swirling in the plasma at the boundary of Jupiter’s magnetosphere, scientists have found.
Data from Juno suggests the Jupiter probe regularly dips through these waves, invisible to the naked eye, as it orbits the giant planet. The discovery helps astronomers understand how mass and energy is transferred from the solar wind to the Jovian planetary environment.
Actually, such waves are not unknown in the Solar System. They’re known as Kelvin-Helmhotz waves, and they occur when there’s a difference in velocity at the boundary between two fluids. They can commonly be seen where wind blows across the surface of lakes and oceans, between currents in water, or even among bands of clouds in a planet’s atmosphere.