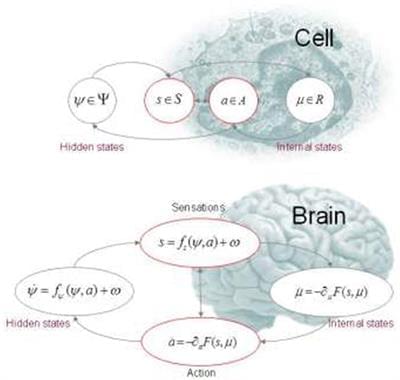
Is self-consciousness necessary for consciousness? The answer is yes. So there you have it—the answer is yes. This was my response to a question I was asked to address in a recent AEON piece (https://aeon.co/essays/consciousness-is-not-a-thing-but-a-process-of-inference). What follows is based upon the notes for that essay, with a special focus on self-organization, self-evidencing and self-modeling. I will try to substantiate my (polemic) answer from the perspective of a physicist. In brief, the argument goes as follows: if we want to talk about creatures, like ourselves, then we have to identify the characteristic behaviors they must exhibit. This is fairly easy to do by noting that living systems return to a set of attracting states time and time again. Mathematically, this implies the existence of a Lyapunov function that turns out to be model evidence (i.e., self-evidence) in Bayesian statistics or surprise (i.e., self-information) in information theory. This means that all biological processes can be construed as performing some form of inference, from evolution through to conscious processing. If this is the case, at what point do we invoke consciousness? The proposal on offer here is that the mind comes into being when self-evidencing has a temporal thickness or counterfactual depth, which grounds inferences about the consequences of my action. On this view, consciousness is nothing more than inference about my future; namely, the self-evidencing consequences of what I could do.
There are many phenomena in the natural sciences that are predicated on the notion of “self”; namely, self-information, self-organization, self-assembly, self-evidencing, self-modeling, self-consciousness and self-awareness. To what extent does one entail the others? This essay tries to unpack the relationship among these phenomena from first (variational) principles. Its conclusion can be summarized as follows: living implies the existence of “lived” states that are frequented in a characteristic way. This mandates the optimization of a mathematical function called “surprise” (or self-information) in information theory and “evidence” in statistics. This means that biological processes can be construed as an inference process; from evolution through to conscious processing. So where does consciousness emerge? The proposal offered here is that conscious processing has a temporal thickness or depth, which underwrites inferences about the consequences of action.