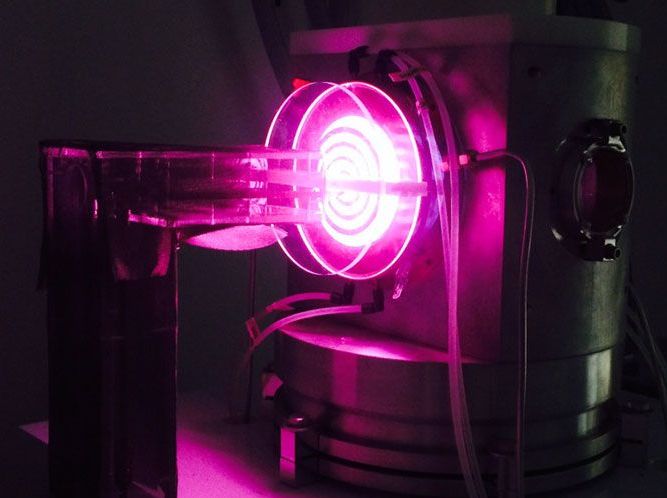
Circa 2019
To create neutrons in the high flux neutron generator, UC Berkeley researchers heat up deuterium atoms in a vacuum chamber to 50000 degrees Celsius to obtain an ionized plasma (pink glow), then accelerate the ions until they collide and fuse with other deuterium atoms implanted in the titanium cathode, releasing neutrons in the process. The spiral coil is the water-cooled radio-frequency antenna that heats the plasma, viewed through a quartz window into the vacuum chamber. (UC Berkeley photo by Cory Waltz)
In an underground vault enclosed by six-foot concrete walls and accessed by a rolling, 25-ton concrete-and-steel door, University of California, Berkeley, students are making neutrons dance to a new tune: one better suited to producing isotopes required for geological dating, police forensics, hospital diagnosis and treatment.
Dating and forensics rely on a spray of neutrons to convert atoms to radioactive isotopes, which betray the chemical composition of a substance, helping to trace a gun or reveal the age of a rock, for example. Hospitals use isotopes produced by neutron irradiation to kill tumors or pinpoint diseases like cancer in the body.