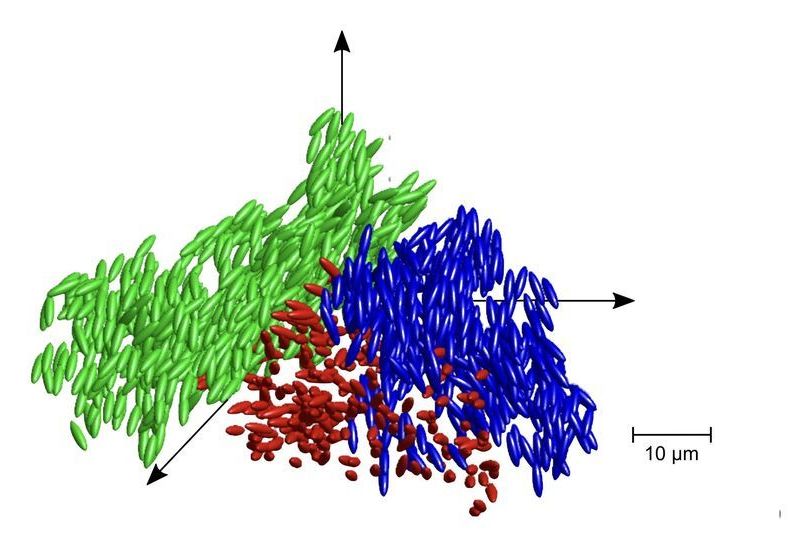
Discovery of liquid glass sheds light on the old scientific problem of the glass transition: An interdisciplinary team of researchers from the University of Konstanz has uncovered a new state of matter, liquid glass, with previously unknown structural elements—new insights into the nature of glass and its transitions.
While glass is a truly ubiquitous material that we use on a daily basis, it also represents a major scientific conundrum. Contrary to what one might expect, the true nature of glass remains something of a mystery, with scientific inquiry into its chemical and physical properties still underway. In chemistry and physics, the term glass itself is a mutable concept: It includes the substance we know as window glass, but it may also refer to a range of other materials with properties that can be explained by reference to glass-like behavior, including, for instance, metals, plastics, proteins, and even biological cells.
While it may give the impression, glass is anything but conventionally solid. Typically, when a material transitions from a liquid to a solid state the molecules line up to form a crystal pattern. In glass, this does not happen. Instead, the molecules are effectively frozen in place before crystallization happens. This strange and disordered state is characteristic of glasses across different systems and scientists are still trying to understand how exactly this metastable state forms.