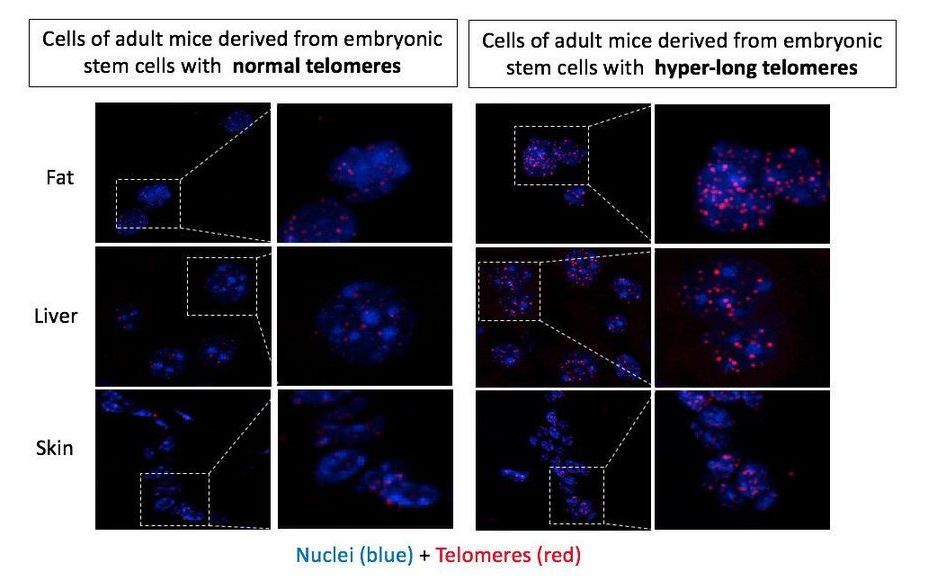
A chance finding 10 years ago led to the creation by researchers of the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) of the first mice born with much longer telomeres than normal in their species. Telomeres shorten throughout life, so older organisms have shorter telomeres. Given this relationship between telomeres and aging, the scientists launched a study generating mice in which 100 percent of their cells had hyper-long telomeres. The findings are published in Nature Communications and show only positive consequences: The animals with hyper-long telomeres live longer and in better health, free from cancer and obesity. This marks the first time that longevity has been significantly increased without any genetic modification.
“This finding supports the idea that, when it comes to determining longevity, genes are not the only thing to consider,” says Maria Blasco, head of the CNIO Telomeres and Telomerase Group and intellectual author of the paper. “There is margin for extending life without altering the genes.”
Telomeres form the ends of chromosomes in the nucleus of each cell in the body. Their function is to protect the integrity of the genetic information in DNA. Whenever the cells divide the telomeres, they are slightly shortened, so one of the main characteristics of aging is the accumulation of shorter telomeres in cells. “Telomere shortening is considered to be one of the primary causes of aging, given that short telomeres cause aging of the organism and reduce longevity,” the authors write in a paper published in Nature Communications.