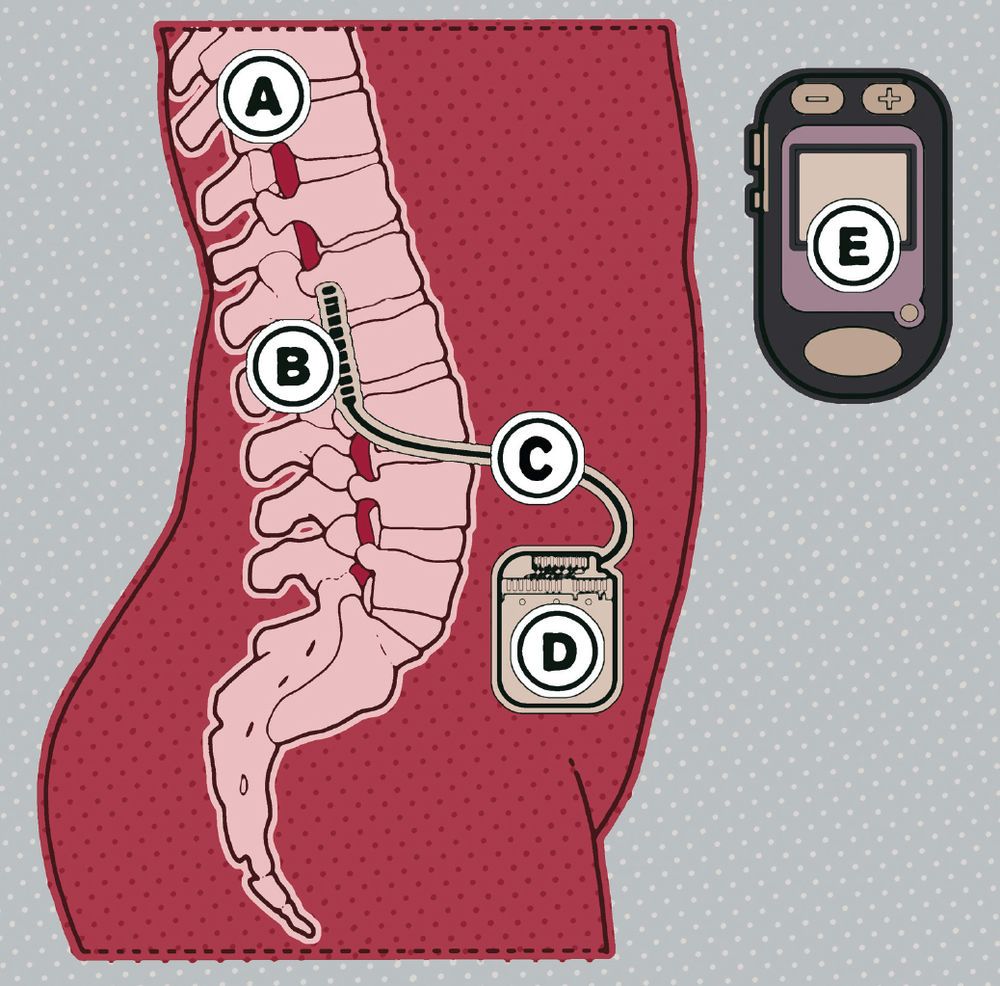
For decades, researchers have been seeking ways to help the millions of people with spinal cord injuries regain control of their limbs, with frustratingly little success. The new device provides a rare glimmer of hope. Scientists at the University of Louisville’s Kentucky Spinal Cord Injury Research Center, where Meas and three other patients received their implants, speculate that the stimulation may be reawakening connections between the brain and the body. “There’s residual circuitry that we can recover that no one realized was possible to do,” says Reggie Edgerton, director of the Neuromuscular Research Laboratory at the University of California, Los Angeles. “We were shocked.”
Some of the benefits, such as better bowel and bladder control and improved blood pressure, remain even when the device is switched off. Electrical stimulation isn’t a cure, of course. The patients still can’t walk. And the stimulation must be customized for each individual, a time-consuming process. But it’s an enormous advance nonetheless. Says Edgerton, “It opens up a whole new mechanism of recovery.”