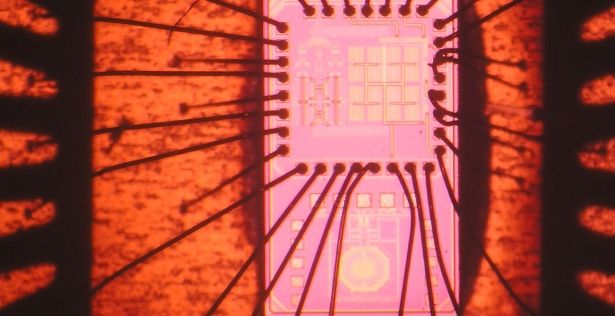
Re-inventing the integrated circuit.
Since the advent of the integrated circuit in 1958, the same year the Advanced Research Projects Agency was established, engineers have been jamming ever more microelectronic integration into ever less chip real estate. Now it has become routine to pack billions of transistors onto chips the size of fingernails.
DARPA (the D for Defense was first added in 1972) has played key roles in this ongoing miracle of miniaturization, giving rise to new and sometimes revolutionary military and civilian capabilities in domains as diverse as communication, intelligence gathering, and optical information processing. Now a DARPA-funded team has drastically miniaturized highly specialized electronic components called circulators and for the first time integrated them into standard silicon-based circuitry. The feat could lead to a doubling of radiofrequency (RF) capacity for wireless communications—meaning even faster web-searching and downloads, for example—as well as the development of smaller, less expensive and more readily upgraded antenna arrays for radar, signals intelligence, and other applications.
The work, funded under DARPA’s Arrays at Commercial Timescales (ACT) program, was led by Columbia University electrical engineers Harish Krishnaswamy and Negar Reiskarimian and described in the April 15, 2016 issue of the journal Nature Communications.